Anti Poverty Measures









Anti Poverty Measures
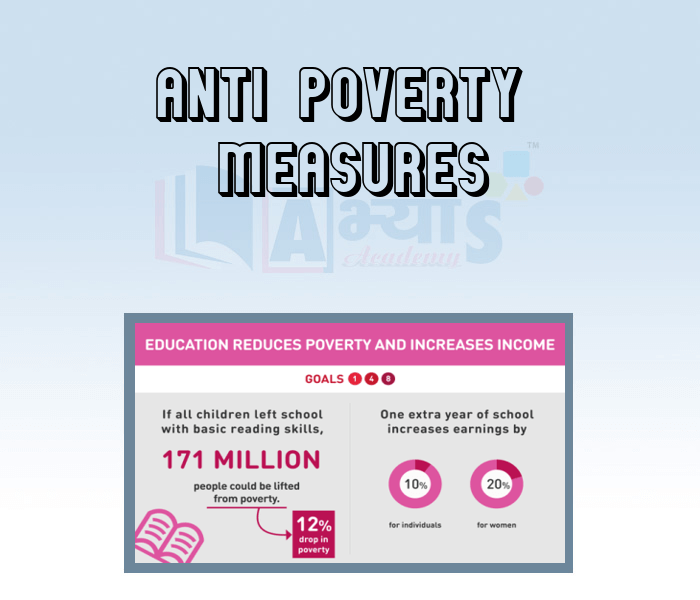
Anti-Poverty Measures:
Removal of poverty has been one of the major objectives of Indian developmental strategy. The current antipoverty strategy of the government is based on following two objectives
1. Promotion of Economic Growth:
The government has promoted economic growth during the last few years. Economic growth was low till the l980s, but has increased significantly since then, causing significant poverty reduction. The high economic growth helps in significant reduction of poverty. There is strong linkage between economic growth and poverty reduction. Economic growth widens opportunities and provides the resources needed to invest in human development. High economic growth encourages people to send their children (including the girl child) to school with hope of better economic returns from investing in education. The poor may not take direct advantage of economic growth. Due to lack of growth in agricultural sector, large numbers of people remain poor in rural areas.
2. Targeted Anti-Poverty Programmes:
The government introduced targeted anti-poverty programmes starting from 1990. The results of these programmes have been mixed due to lack of proper implementation and improper targeting. Also, some schemes overlap others. Thus, the benefits of these schemes are not fully reaching the deserving poor. So, now the government is emphasising more on proper monitoring of all these programmes.
Millennium Development Goals:
These are eight international development goals that were officially established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. One of these was to reduce by 50% the proportion of people living on less than US $1 a day by the year 2015.
Poverty Prevention Measures
1. Poverty prevention efforts through Five Year Plans.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
One of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice
